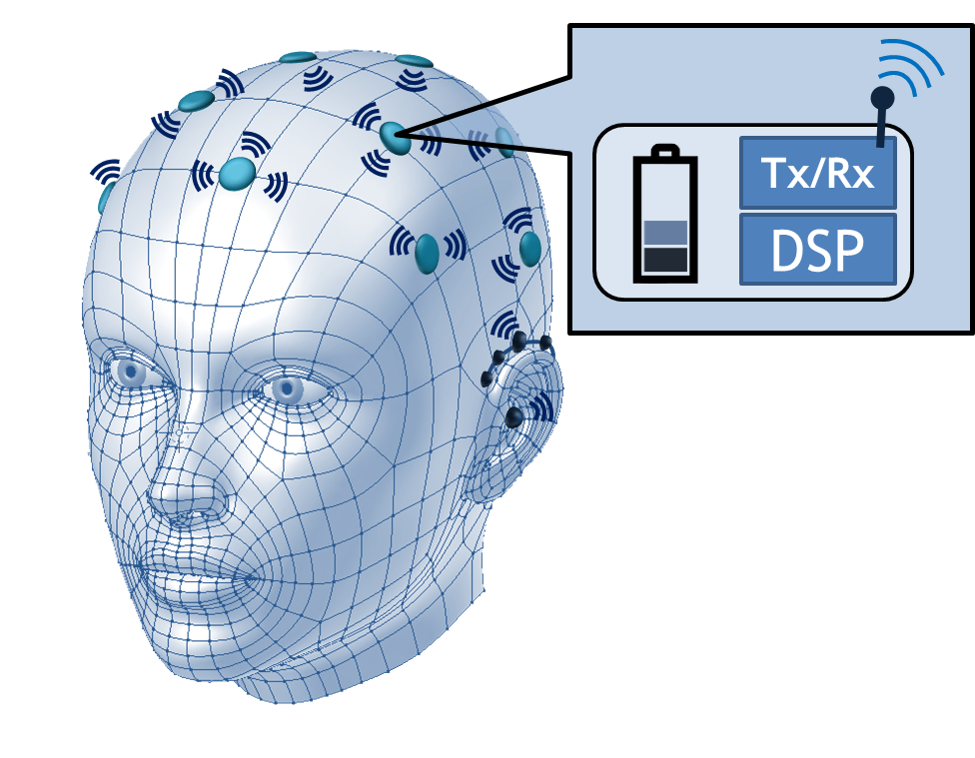
One specific goal of the group is the development of the Wireless EEG Sensor Network (WESN). EEG is the measurement of the electrical activity of the brain, a highly useful signal in a variety of applications such as epileptic seizure detection, sleep monitoring or brain-computer interfaces. In contrast to the traditional, bulky EEG cap required for such measurements, the WESN is composed of a number of lightweight, concealable mini-EEG devices organized in a wireless sensor network. The user-friendly and modular nature of the WESN makes it a very promising avenue for continuous neuromonitoring in daily life. However, this new setting also comes with algorithmic challenges. Thus, we investigate the use of new distributed signal processing algorithms to allow the different sensor nodes to cooperate in an energy-efficient way.
